One-sentence summary
We are going to talk about Otis today because of the hurricane’s dramatic intensification on Tuesday, and overnight landfall along the Southern Pacific coast of Mexico.
Rapid intensification
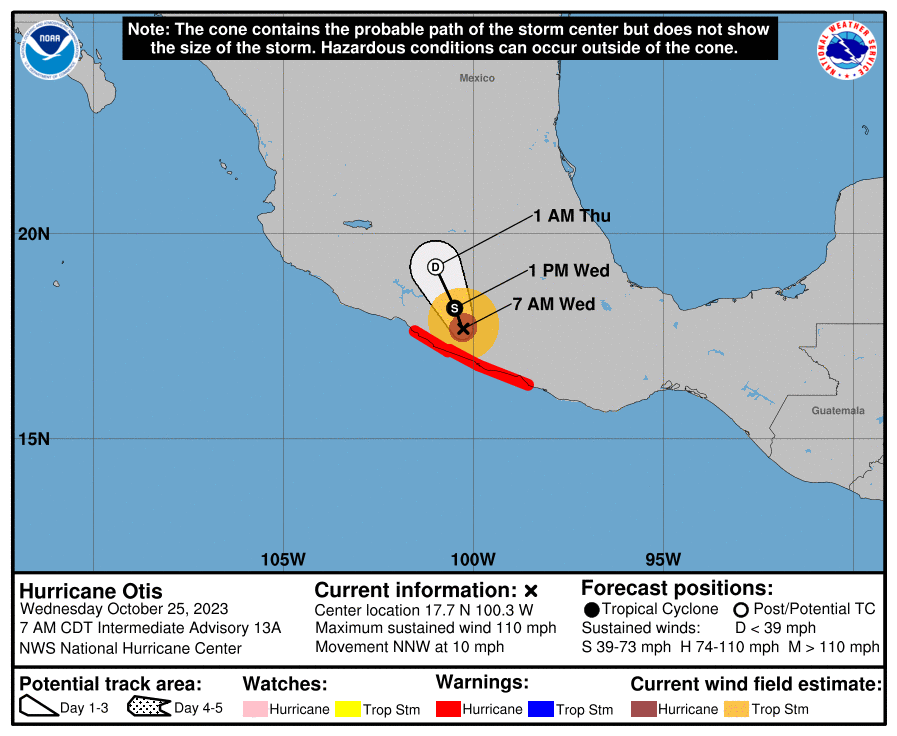
Otis made landfall on Tuesday night, near Acapulco, with maximum sustained winds of 165 mph. This was a worst-case scenario for this region. Why? Because no storms had been recorded in this area, this strong, before. On top of that, local residents and business owners had less than a day to prepare for the worst hurricane of their lives. So not only was this storm unexpected, there was no institutional memory about what to expect from a major hurricane.
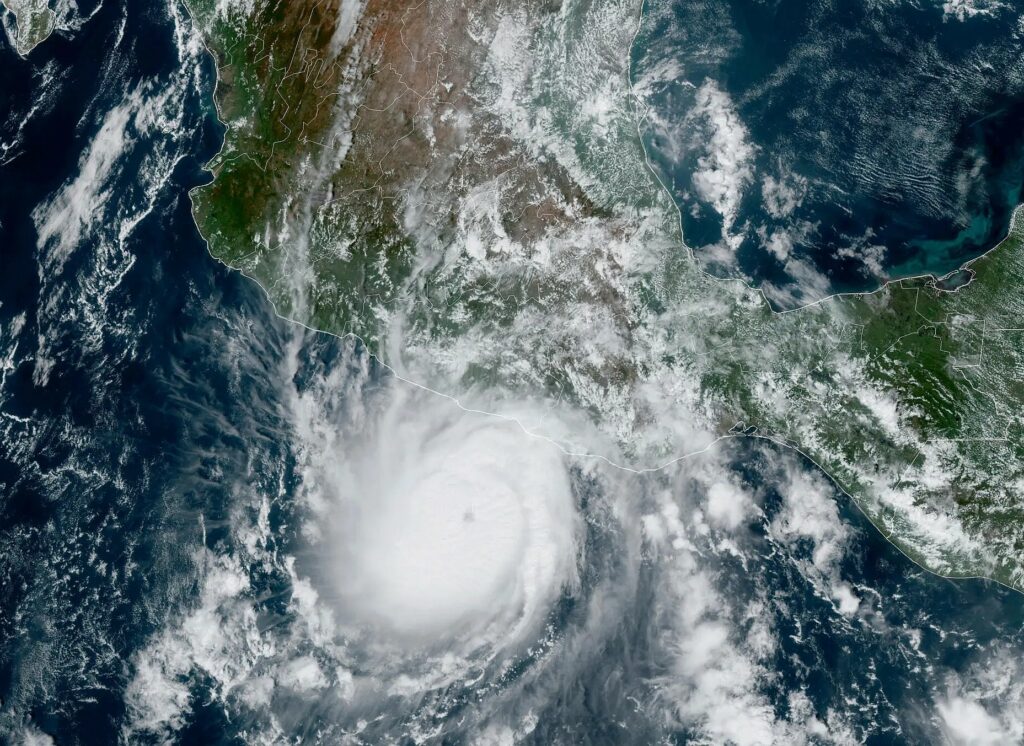

With this startling burst in intensity, Otis has nearly set a record for rapid intensification within 24 hours. The system strengthened from a 50 mph tropical storm at 1 am CT on Tuesday to 165 mph just 23 hours later. That is 115 mph in 24 hours. It is second only to Hurricane Patricia, a Pacific storm in 2015 that saw its maximum sustained winds increase by 120 mph during a similar period.
This morning, as it moves inland, Otis is weakening. As of 7 am CT the storm had 110 mph winds, and will continue to lose intensity as it interacts with mountainous terrain. Nevertheless, Otis will continue to bring damaging winds into Southern Mexico today, along with dangerous storm surge. Heavy rains will remain a problem later this week, through Thursday, for much of Southern Mexico. They are likely to produce significant flooding and mudslides.
Completely blind-sided
Let’s wind things back to Monday night, and have a look at the model forecasts for the intensity of Hurricane Otis. At the time this was a tropical storm, and largely expected to remain so before its landfall into Mexico. None of our ‘best’ models for predicting tropical system intensity anticipated Otis growing beyond tropical storm-strength. In two decades of forecasting I do not recall a whiff like this one.
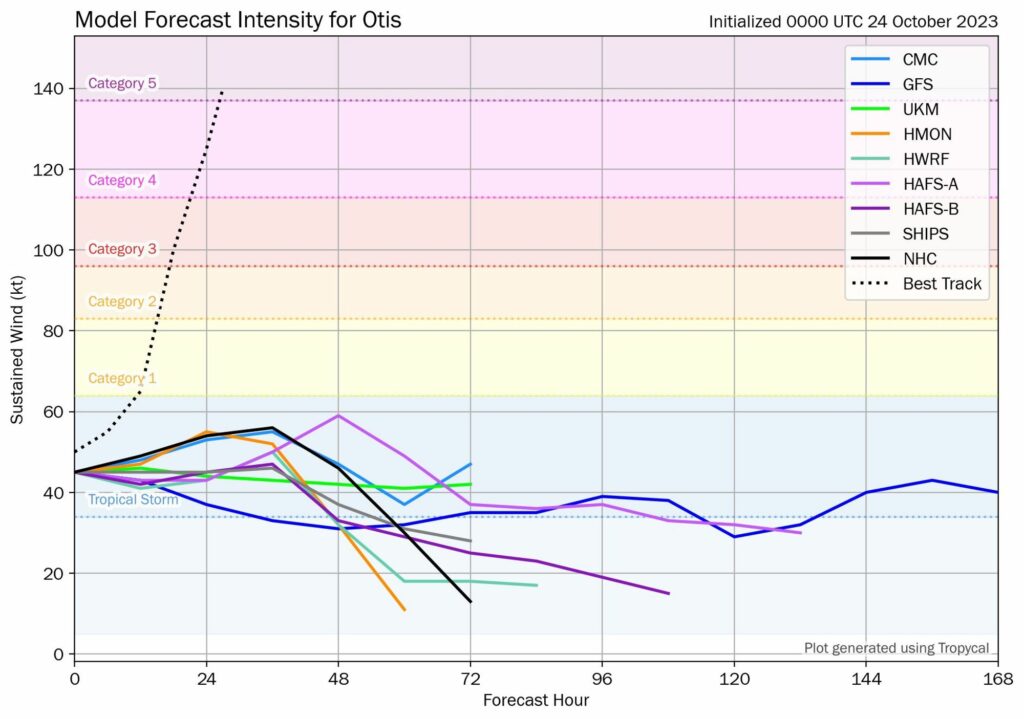
As a meteorologist, these kind of moments are humbling. Otis will be studied in the coming months and years to understand why it blew up so quickly, and so powerfully, in such a short period of time. In moments like these, forecasters utterly failed the people of Southern Mexico. We must do better.
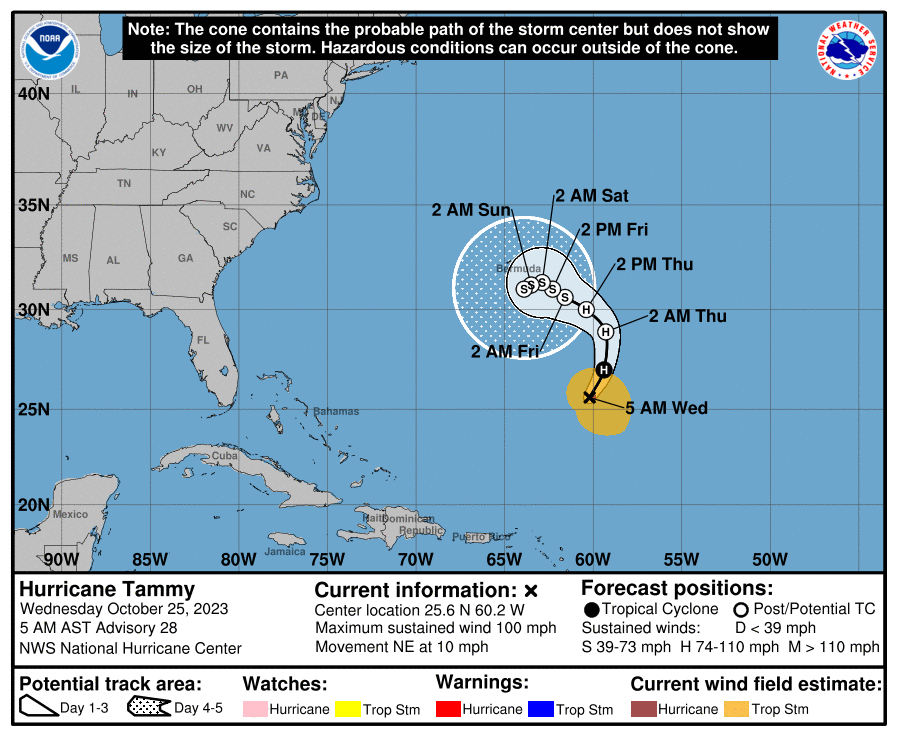
Hurricane Tammy
Over in the Atlantic Ocean, Hurricane Tammy continues to dance around the Atlantic Ocean. This storm would be a curiosity given its meandering track, but for its potential to come near Bermuda this weekend. As of Wednesday morning, Tammy has sustained winds of 100 mph, and there is a chance for some slight strengthening today.
However, after today it is likely to interact with a cold front, and begin a transition to a non-tropical storm. There is a fair amount of uncertainty in track and intensity. But for now it looks like Tammy will remain far enough south, and just weak enough, to not bring anything more than garden-variety like storminess to Bermuda this weekend.
Beyond Tammy, happily, the Atlantic tropics look quiet.